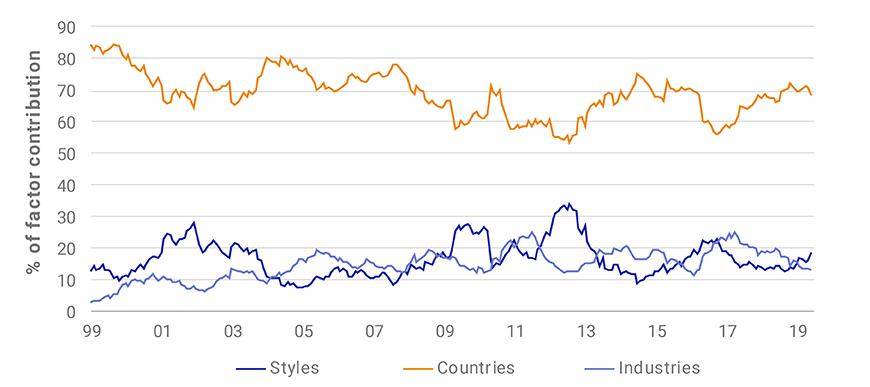
Cross Sectional Volatility
This dispersion measure is of fundamental importance as it represents the opportunity set for active portfolio management.
Cross sectional volatility. A risk factor volatility carry strategy fully explains the cross sectional variation of slope sorted volatility excess returns. Cross sectional volatility measures the dispersion of security returns or the extent to which companies share prices react differently to market events. Cross sectional volatility index as a proxy for aggregate economic uncertainty which suggests that the correlation between systematic volatility and average idiosyncratic volatility should be high which we confirm empirically.
3 3 recent studies examining total or idiosyncratic volatility focus on the average level of firm level volatility. For instance if the dispersion of stock returns is very small. Cross sectional volatility is given by the standard deviation of a set of asset returns over a single time period.
In this research insight we present an exact methodology for decomposing csv into contributions from individual factors. Cross sectional volatility specifically addresses. Cross sectional analysis may focus on a single.
This table reports cross sectional regressions with total return volatility vol and idiosyncratic volatility ivol of bonds panel a or stocks panel b. The second goal of the paper is to examine the cross sectional relationship between idiosyncratic volatility and expected returns where idiosyncratic volatility is defined relative to the standard fama and french 1993 model. When stock prices move in different directions cross vol is higher.
When all stocks move up or down together cross vol is lower. Cross sectional regressions with total and idiosyncratic return volatilities. Effective evaluation of reported active manager return results.
When cross sectional volatility is high the investment opportunity set expands and could impact the size of. Volatility and volatility indices. Finally section 6 concludes.