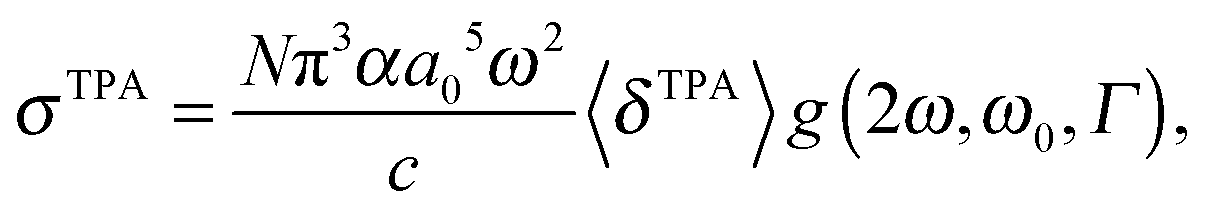Absorption Cross Section Equation

The sum of the absorption and scattering cross sections is sometimes referred to as the extinction cross section.
Absorption cross section equation. In terms of area the total cross section σ is the sum of the cross sections due to absorption scattering and photoluminescence. This is illustrated by σ 1000ln 10 ε n a 3 82 x 10 21 ε. Its values are constant at a particular wavelength and concentration for a given species.
σ μ ρ m a n a. By converting photon density into intensity i ρ ν c the final equation can be written in terms of an intensity ratio i i 0. The relevant free free transition integrals have been computed and from the tables given the free free absorption cross section for an electron in the field of a positive ion can be readily.
The absorption cross section is closely related to molar absorptivity and mass absorption coefficient. Absorption cross section of acridine orange dye at 430 nm is σ 10 16 cm 2 molar absorption 27000 m 1 cm 1. For a given particle and its energy the absorption cross section of the target material can be calculated from mass absorption coefficient using.
Some peculiar effects here have to be taken into account. Where σi e barn is the microscopic neutron absorption cross section for the i absorber nuclide of the material and ni is the concentration at cm 3. This formula or equation can be used only when you know the absorption cross section.
7 5 6 α total energy absorbed per unit time total incident intensity energy unit time area 7 5 7 ℏ ω w k ℓ i. Note α has units of cm 2. 1 2 1 1 2 dddt b n dx dt dx c b c ρνρν ρν σ 1 00 1 0 ln ll l d ndx ln ρν σ ρν ρν σ ρν the total change in the photon density over a distance l is obtained by integration.